Linked List – संकल्पना समजून घेऊया!
Linked List – संकल्पना समजून घेऊया!
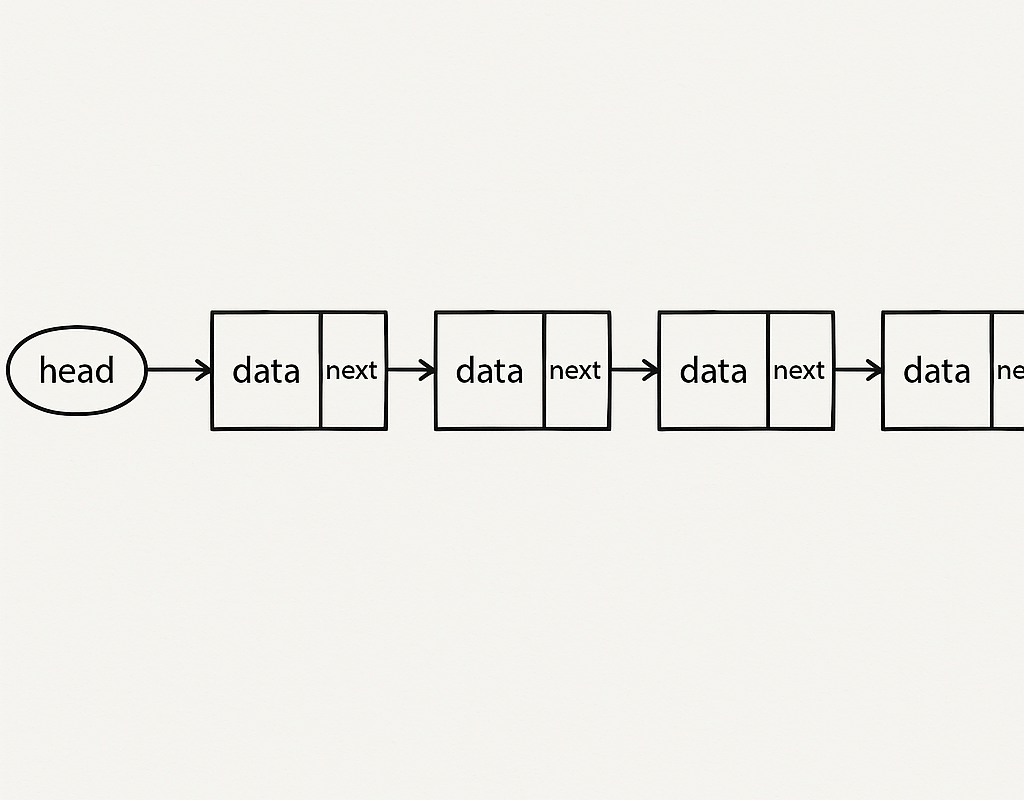
What is a Linked List?
Definition (English):
A Linked List is a non-contiguous linear data structure where elements (called nodes) are connected via pointers.
म्हणजे नेमकं काय? (Marathi):
Linked List म्हणजे एक अशी data structure जिच्यात data एका ठिकाणी न ठेवता, प्रत्येक data ला त्याच्या पुढच्या data चा पत्ता (address/pointer) दिलेला असतो.
उदाहरण:
समजा तुमच्याकडे एक गाडी आहे जी पत्त्यावर जाऊन पार्सल देते (जसं Swiggy delivery). तुम्ही गाडीला फक्त पहिलं पार्सल कुठे द्यायचं ते सांगता — पुढचा पत्ता त्या पहिल्या पार्सलमध्येच दिलेला असतो. अशीच Linked List मध्ये एक node दुसऱ्या node चा address ठेवते.
Linked List vs Array Comparison
| Feature | Linked List (लिंक्ड लिस्ट) | Array (अॅरे) |
| Memory Structure | Non-contiguous (विखुरलेली) | Contiguous (सलग) |
| Memory Allocation | Dynamic – node by node | Static – एकदम सगळी जागा एकत्र |
| Insertion/Deletion | Fast (O(1)/O(n)) | Slow (O(n)) |
| Access Type | Sequential (एकामागोमाग) | Random (तयार index वरून) |
| Resize Karaycha Ka? | नको – Dynamic असते | लागेल – Array fix size असतो |
Types of Linked Lists (Linked List चे प्रकार)
- Singly Linked List (एकेरी लिंक्ड लिस्ट):
एका node मध्ये data + पुढच्या node चा pointer असतो. - Doubly Linked List (दुहेरी लिंक्ड लिस्ट):
प्रत्येक node मध्ये मागच्या आणि पुढच्या दोघांचे pointers असतात. - Circular Linked List (परिपूर्ण साखळी):
शेवटचा node पुन्हा सुरुवातीच्या node कडे point करतो.
Applications & फायदे:
- Stack, Queue, Deque सारखे structures तयार करायला वापरतात.
- Dynamic memory असलेलं environment (जसं कि embedded systems) मध्ये फायदेशीर.
- Real-life वापर:
- Browser History (Doubly Linked List)
- Undo/Redo (Linked List + Stack)
- Music Playlist (Circular List)
Operations on Linked List (Linked List वर क्रिया):
Basic Operations:
- getLength() – लिस्ट किती लांब आहे?
- printList() – संपूर्ण लिस्ट print करायची.
- insertNode(data, pos) – data insert करा.
- deleteByValue(val) – दिलेलं value delete करा.
- deleteAtPosition(pos) – दिलेल्या position वरून node काढा.
- search(value) – value लिस्ट मध्ये आहे का?
- deleteList() – संपूर्ण लिस्ट delete करा.
- getNthFromStart(n) – सुरुवातीपासून nth node.
- getNthFromEnd(n) – शेवटीपासून nth node.
Easy Level Problems: (सोपे प्रश्न)
- Every K-th node काढून टाका.
- Middle node शोधा.
- Count Occurrences of a value.
- Circular List traverse करा.
- Check circularity (साखळी पूर्ण आहे का?)
- Circular मध्ये node काढा.
- Singly ↔ Circular conversion.
- पहिला व शेवटचा node exchange करा.
- Doubly Linked List Reverse करा.
Medium Level Problems: (मध्यम स्तर)
- Swap nodes in pairs
- Loop detection
- Loop चं length
- Browser History design
- Remove duplicates (sorted & unsorted)
- Merge Two Sorted Linked Lists
- Rotate linked list
- QuickSort / MergeSort on List
- Intersection & Union of lists
- Split circular list into 2
- Insert in sorted order (DLL)
- Delete with only pointer
- Segregate even & odd
Hard Level Problems: (अवघड समस्या)
- Merge K sorted lists
- Linked List intersection point
- LRU Cache Implementation
- Josephus Circle Problem
- Tree to Doubly Linked List Conversion
- Clone List with Random Pointer
- Sublist Search
- Multiply two numbers represented as Linked Lists
- Group-wise Reverse of List
- Block-wise Rotate Linked List
- Matrix to Linked List conversion
TECHNORBIT NOTE:
तुम्ही Linked List शिकताना visualization करा – प्रत्येक node म्हणजे एक पर्सनल courier package आणि pointer म्हणजे पत्ता.
एक node दुसऱ्याकडे जातो म्हणजे तो पुढचा पत्ता सांगतो – अगदी जसं chain reaction.
TECHNORBIT नेहमी सांगतो:
“Code म्हणजे जादू आहे, पण Logic ही त्याची जादूची कांडी!”
Singly Linked Problem
Singly Linked List म्हणजे एक linear data structure जिथे प्रत्येक node मध्ये data आणि पुढच्या node चा address (pointer) असतो. शेवटचा node `NULL` ला point करतो.
Diagram:
+——+ +——+ +——+ +——+
| 10 | -> | 20 | -> | 30 | -> | NULL |
+——+ +——+ +——+ +——+
Real-Time Use Case:
Music Playlist: एक गाणं संपल्यावर दुसरं सुरु होतं. त्याच logic प्रमाणे, playlist ही Singly Linked List सारखीच असते.
Singly Linked List in C Language
include <stdio.h>
include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node next;
};
// Function to print linked list
void printList(struct Node head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main() {
struct Node head = NULL;
struct Node second = NULL;
struct Node third = NULL;
// Memory allocation
head = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 10;
head->next = second;
second->data = 20;
second->next = third;
third->data = 30;
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
10 -> 20 -> 30 -> NULL
Practice Questions:
- एक node insert करा सुरुवातीला, मध्ये आणि शेवटी.
- एखादी value शोधा (`search()` function).
- एखादी value delete करा.
- Singly List reverse करा.
Trick:
- Linked List म्हणजे data ची साखळी — एका node ने दुसऱ्याला धरून ठेवलेलं असतं. जर पहिला node हातातून गेला, तर पूर्ण साखळी तुटते — त्यामुळे `head` ची काळजी घ्या!
- Singly Linked List म्हणजे एक linear data structure जिथे प्रत्येक node मध्ये data आणि पुढच्या node चा address (pointer) असतो. शेवटचा node `NULL` ला point करतो.
- Doubly Linked List मध्ये प्रत्येक node मध्ये data, पुढच्या आणि मागच्या node चा pointer असतो. यामुळे दोन्ही दिशेने traversal शक्य होतं.
- Circular Linked List मध्ये शेवटचा node पहिल्या node कडे परत point करतो — यामुळे साखळी circle मध्ये बदलते.
Linked List
NULL <-+——+<->+——+<->+——+-> NULL
| 10 | | 20 | | 30 |
+——+ +——+ +——+
Circular Linked List
+——+ +——+ +——+
| 10 | -> | 20 | -> | 30 |
+——+ +——+ +——+
^ |
|———————-|
Real-Time Use Cases:
Music Playlist: एक गाणं संपल्यावर दुसरं सुरु होतं (Singly).
Browser History: मागे व पुढे navigate करणं शक्य (Doubly).
Carousel/Slides: circular design जिथे शेवट नंतर पहिला item येतो (Circular).
Doubly Linked List in C Language
include <stdio.h>
include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node prev;
struct Node next;
};
void printList(struct Node node) {
struct Node last;
printf("Forward: ");
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
printf("Backward: ");
while (last != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", last->data);
last = last->prev;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main() {
struct Node head = NULL;
struct Node second = NULL;
struct Node third = NULL;
head = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 10; head->prev = NULL; head->next = second;
second->data = 20; second->prev = head; second->next = third;
third->data = 30; third->prev = second; third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
Forward: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> NULL Backward: 30 -> 20 -> 10 -> NULL
Circular Linked List in C
include <stdio.h>
include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node next;
};
void printList(struct Node head) {
struct Node temp = head;
if (head != NULL) {
do {
printf("%d -> ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
}
printf("(back to head)\n");
}
int main() {
struct Node head = NULL;
struct Node second = NULL;
struct Node third = NULL;
head = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = (struct Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 10; head->next = second;
second->data = 20; second->next = third;
third->data = 30; third->next = head;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> (back to head)
Practice Questions:
- Singly, Doubly, Circular List मध्ये insert करा सुरुवातीला, मध्ये आणि शेवटी.
- एखादी value शोधा (`search()` function).
- एखादी value delete करा.
- Singly, Doubly List reverse करा.
- Detect circular loop in linked list.
- Find middle of linked list.
- Merge two sorted linked lists.
TECHNORBIT Trick:
Linked List म्हणजे data ची साखळी — एका node ने दुसऱ्याला धरून ठेवलेलं असतं. जर पहिला node हातातून गेला, तर पूर्ण साखळी तुटते — त्यामुळे `head` ची काळजी घ्या!